Advantages and Disadvantages of Absolute Liquidity Ratio
Absolute liquidity ratio is the financial ratio used to evaluate the company liquidity ratio. Similar to the current and quick ratio, it accesses the company’s ability to pay off the current liabilities. However, the absolute liquidity ratio uses only the cash and marketable securities and temporary investment which can be converted to cash very easily.
The absolute liquidity ratio only uses only the super quick currents assets which can be converted to cash within a very short time.
Absolute Liquidity Ratio Formula
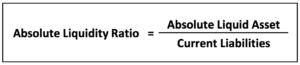
Absolute Liquid Asset = Cash & Cash Equivalent + Marketable Securities
Advantages of Absolute Liquidity Ratio
- Easy to calculate: the calculation is very easy and straightforward, it does not require any special data or accounting software to support it.
- Easy to Analyze: Most of the company prefer to have a ratio of 0.5 to 1 which show strong financial health as the company has enough cash to pay for the current liabilities.
- Measure the company liquidity:
- More Accurate: If we compare this ratio to the current and quick ratio, it is more reliable as we have excluded any current assets which are hard to convert to cash such as inventory, prepaid expenses, and so on.
Disadvantages of Absolute Liquidity Ratio
- Only using cash and marketable security: Even the cash and marketable securities are the current assets that easily convent to cash, but rely only upon them to access the whole company liquidation is very subjective.
- No other liquidity current asset: We have excluded other current assets even they can easily convert to cash. Some companies can convert the inventory to cash in less than a month. So by excluding them, we cannot see the whole company’s financial health.
- Cannot provide absolute assessment: Use only this ratio, we cannot make any judgment relate to company liquidation. The company has a very low ratio, but they have other sources of cash flow such as loans or capital which will allow them to operate without any worry.
- Rely on the past data: Basically, the ratio depends on the company’s past performance and it is very challenging to use this data for making a future decision.