Bond Discount Journal Entry
Overview
It is not strange for a company to issue the bond at a discount, in which the selling price of the bond is lower than its face value. Likewise, the company will make the journal entry to account for the bond discount by debiting the amount of the difference between the face value of a bond and its selling price in the unamortized bond discount account.
The company usually issues the bond at a discount when the market rate of interest is higher than the contractual interest rate of the bond. After all, investors are unlikely to pay for the bonds at the face value if they can invest in other securities with similar risks but providing a better rate of return.
Bond discount journal entry
When the company issues a bond at the discount, it can make the bond discount journal entry by debiting the cash account and the unamortized bond discount account and crediting the bonds payable account.
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | $$$ | |
| Unamortized bond discount | $$$ | |
| Bonds payable | $$$ |
Unamortized bond discount is a contra account to bonds payable which its normal balance is on the debit side. Likewise, the balance in this unamortized bond discount will be presented as a deduction from the bonds payable on the balance sheet.
Under the matching principle of accounting, the bond discount should be amortized over the life of the bond; hence, the term “unamortized bond discount” is used here. Likewise, with the amortization, the balance of the unamortized bond discount will be reduced throughout the life of the bond until it becomes zero at the end of bond maturity.
Bond discount example
For example, on February 1, the company ABC issues a $100,000 bond with a five-year period at a discount which it sells for $97,000 only. The bond gives an 8% interest which is payable annually on February 1.
In this case, the company ABC can make the bond discount journal entry on February 1, when it issues the bond at a discount as below:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | 97,000 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 3,000 | |
| Bonds payable | 100,000 |
It is useful to note that the unamortized bond discount account may also be called “bond discount” or “discount on bonds payable”. Though, the term “unamortized bond discount” here can also be used as a reminder, so that the company does not forget to amortize the bond discount in order to comply with the matching principle of accounting.
Amortization of bond discount
As mentioned, the unamortized bond discount is a contra account to the bonds payable on the balance sheet. Likewise, the carrying value of the bonds payable equals the balance of bonds payable less the balance of the unamortized bond discount.
| Carrying value of bonds payable on the balance sheet | |
| Bonds payable | $$$ |
| Less: unamortized bond discount | ($$$) |
| Carrying value of bonds payable | $$$ |
And the amortization of bond discount will increase the carrying value of the bonds payable on the balance sheet from one period to another until it equals the face value of the bond at the end of the bond maturity. After all, at the end of the bond maturity, the balance of the unamortized bond discount will become zero.
The company can make the journal entry for the amortization of bond discount by debiting the interest expense account and crediting the unamortized bond discount account.
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | $$$ | |
| Unamortized bond discount | $$$ |
The amortization of bond discount can be done with the straight-line method or the effective interest rate method depending on if the amount of discount is material or not. If the discounted amount is material the company need to amortize the bond discount with the effective interest rate method as it is a more accurate method compared to the straight-line method.
Example for amortization of bond discount
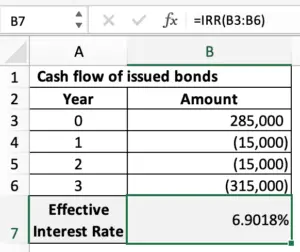
For example, the company ABC issued $300,000 bonds at a discount for only $285,000 which is 95% of their face value. These bonds have a maturity of three years with an interest rate of 5% per annum that is payable annually.
Based on the discounted future cash flows of the $300,000 bonds that have been issued, the effective interest rate can be calculated to be 6.9018% per annum.
What is the journal entry for the amortization of bond discount for the three years using:
- Straight-line method
- Effective interest rate method
Solution:
The company ABC can make the journal entry for issuing the $300,000 bonds at a discount as below:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | 285,000 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 15,000 | |
| Bonds payable | 300,000 |
Amortization using the straight-line method
Using the straight-line method, we can calculate the amortization amount to be $5,000 per year ($15,000 / 3 years).
In this case, the company ABC can make the journal entry for amortization of bond discount under the straight-line method for the three years as below:
Year 1:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | 5,000 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 5,000 |
Year 2:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | 5,000 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 5,000 |
Year 3:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | 5,000 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 5,000 |
At the end of the third year, the balance of the unamortized bond discount will become zero ($15,000 – $5,000 – $5,000 – $5,000) and the carrying value of bonds payable at the end of the maturity will equal their face value of $300,000.
Amortization using the effective interest rate method
With the effective interest rate of 6.9018% per annum, the amortization of bond discount can be calculated as in the table below:
| Year | Bonds Payable | Discount | Carrying Value | Interest payment | Interest expense | Amortization |
| 0 | 300,000 | 15,000 | 285,000 | – | – | – |
| 1 | 300,000 | 10,330 | 289,670 | 15,000 | 19,670 | 4,670 |
| 2 | 300,000 | 5,337 | 294,663 | 15,000 | 19,993 | 4,993 |
| 3 | 300,000 | 0 | 300,000 | 15,000 | 20,337 | 5,337 |
| Total | 45,000 | 60,000 | 15,000 |
*Interest payment = $300,000 x 5% = $15,000
**Interest expense – first year = $285,000 x 6.9018% = $19,670
***Amortization – first year = $19,670 – $15,000 = $4,670
Likewise, the company ABC can make the journal entry for the amortization of bond discount using the effective interest rate method for three years as below:
Year 1:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | 4,670 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 4,670 |
Year 2:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | 4,993 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 4,993 |
Year 3:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | 5,337 | |
| Unamortized bond discount | 5,337 |
In this case, we can see the difference between the amortization of bond discount using the straight-line method and the one using the effective interest rate method as below:
| Year | Straight-line | Effective interest rate | Difference |
| 1 | 5,000 | 4,670 | 330 |
| 2 | 5,000 | 4,993 | 7 |
| 3 | 5,000 | 5,337 | (337) |
| Total | 15,000 | 15,000 | 0 |
Note:
The effective interest rate of 6.9018% can be calculated using the IRR() formula from the excel spreadsheet as below: